Xiamen TJ Metal Material Co., Ltd. (referred to as TJ Company) was established in 2009 and is now an important private backbone enterprise in Fujian Province, headquartered in Xiamen City, Fujian Province.
Graphene Oxide Foam – A Professional Material Introduction
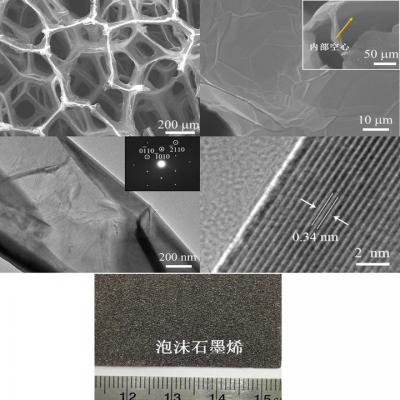
Graphene oxide foam (GO foam) is an emerging threedimensional (3D) carbonbased material engineered by assembling graphene oxide nanosheets into a highly porous, lightweight, and mechanically robust structure. As an advanced derivative of graphene oxide, GO foam combines the exceptional surface chemistry of graphene oxide with the advantages of macroscopic porous frameworks. This unique configuration grants the material excellent adsorption capacity, tunable wettability, large specific surface area, and strong chemical reactivity, making it valuable in energy storage, environmental remediation, catalysis, thermal management, and composite reinforcement.
1. Concept of Graphene Oxide Foam
Graphene oxide foam is formed by crosslinking and assembling graphene oxide flakes into a 3D interconnected network. Graphene oxide contains abundant oxygencontaining functional groups—such as hydroxyl, epoxide, carbonyl, and carboxyl groups—distributed on its basal plane and edges. These functional groups enable strong hydrophilicity, adjustable surface charge, and versatile chemical modification, making GO foam highly adaptable for structural and functional applications. Because the foam is ultralightweight and typically exceeds 90% porosity, it exhibits properties that cannot be achieved by traditional bulk carbon materials.
2. Structural Characteristics
The structure of graphene oxide foam can be summarized in several aspects:
• 3D Porous Framework
The foam contains interconnected macro, meso, and micropores, providing a hierarchical network that maximizes accessible surface area and masstransport pathways.
• OxygenFunctionalized Carbon Sheets
The presence of oxygen groups facilitates chemical bonding, adsorption interactions, metal ion chelation, and catalytic activity.
• Tunable Density and Porosity
GO foam density typically ranges from 5–50 mg/cm³, depending on preparation conditions such as freezedrying rate, GO concentration, and reduction methods.
• Mechanical Integrity
Despite its low density, the foam often exhibits elastic recovery, compressibility, and structural stability due to the crosslinked graphene oxide architecture.
• Thermal and Electrical Modifiability
GO foam is electrically insulating in its fully oxidized state, but can be thermally or chemically reduced to enhance conductivity.
3. Key Material Properties
• High Surface Area
Large internal surface area provides abundant active sites for adsorption, catalysis, and electrochemical reactions.
• Strong Chemical Reactivity
Oxygen functional groups allow surface modification, doping, metal nanoparticle loading, and polymer grafting.
• Excellent Sorption Capability
GO foam absorbs organic pollutants, oils, dyes, and heavy metal ions due to hydrophilicity and electrostatic interactions.
• Thermal Stability
Although not as heatresistant as reduced graphene foam, GO foam remains stable up to ~200°C and can be engineered for higher temperature resistance.
• Adjustable Electrical Properties
Electrical conductivity can be tuned from insulating (GO) to semiconductive or conductive after reduction (rGO foam).
• Lightweight & Flexible
Its low density and compressibility make it suitable for wearable, flexible, and portable devices.
CVD Graphene Materials
4. Preparation and Processing Techniques
Several fabrication methods are used to produce graphene oxide foam:
• FreezeDrying (Cryogel Method)
GO dispersions are frozen and sublimated, creating lightweight aerogellike structures with uniform pore distribution.
• Hydrothermal Assembly
GO undergoes partial reduction and selfassembly into a 3D monolith under high temperature and pressure.
• Chemical or Thermal Reduction
Posttreatment reduces GO to rGO, enhancing conductivity while maintaining the foam's structure.
• TemplateAssisted Methods
Templates like polymer spheres or metal foams shape the pore structure before being removed.
• Crosslinking and Polymer Integration
GO sheets can be crosslinked with polymers or metal ions to strengthen mechanical properties or add functionality.
Each process allows specific tailoring of density, pore morphology, and surface chemistry depending on the intended application.
5. Applications of Graphene Oxide Foam
• Environmental Remediation
GO foam efficiently adsorbs dyes, heavy metals, radioactive ions, and organic pollutants due to its affinity for water and charged molecules.
• Energy Storage and Conversion
Used as electrodes or support materials in batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells, often after partial reduction to enhance conductivity.
• Catalytic Supports
Its high surface area enables loading of metal nanoparticles for catalytic reactions such as hydrogen evolution, CO₂ reduction, or organic synthesis.
• Thermal Management
The foam’s porous structure makes it suitable for insulation, heat dissipation substrates, and lightweight thermal interfaces.
• Biomedical Applications
GO foam can serve in drug delivery, biosensors, tissue engineering scaffolds, and antimicrobial materials thanks to its tunable surface chemistry.
• Composite Reinforcement
GO foam strengthens polymers, ceramics, and metals by providing a highsurfacearea 3D reinforcing skeleton.
6. Advantages of Graphene Oxide Foam
• UltraLow Density
Provides exceptional massspecific performance and serves as a lightweight reinforcement material.
• Highly Customizable Surface Chemistry
Functional groups enable molecularlevel design for tailored interaction with various substances.
• Superior Adsorption Performance
High porosity and chemical affinity make it ideal for filtration and purification.
• Scalable Preparation
GO foam is easier and less costly to produce than pure graphene foam.
• Versatility
Can be used in energy devices, environmental engineering, composites, and catalysis.
• CostEffective Alternative to Graphene Foam
Because GO is cheaper and easier to process, GO foam provides similar advantages at lower production cost.
Conclusion
Graphene oxide foam is a multifunctional, lightweight, and chemically versatile 3D material that exhibits remarkable properties derived from its porous architecture and oxygenrich surface structure. With tunable mechanical, thermal, and chemical characteristics, GO foam is increasingly used across environmental science, energy storage, catalysis, composites, and biomedical fields. Its scalability and modifiability make it a promising platform material for nextgeneration technological applications.