Xiamen TJ Metal Material Co., Ltd. (referred to as TJ Company) was established in 2009 and is now an important private backbone enterprise in Fujian Province, headquartered in Xiamen City, Fujian Province.
3D Graphene Foam – Professional Material Introduction
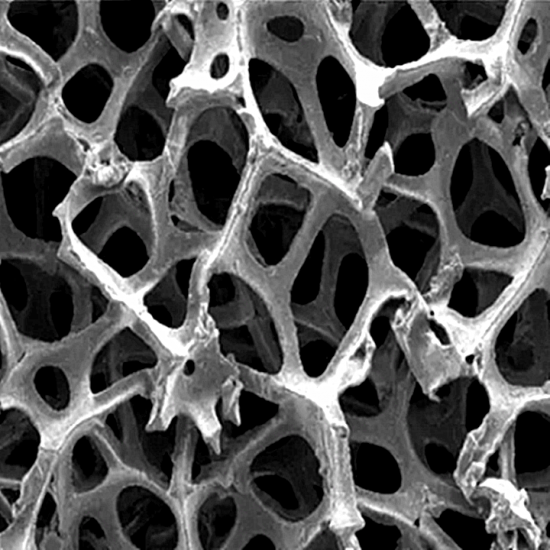
3D graphene foam is an advanced carbonbased material engineered with a threedimensional interconnected porous architecture composed of graphene sheets. This unique structural design offers exceptional properties such as ultrahigh surface area, excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, superior mechanical strength, and remarkable chemical stability. Owing to its lightweight nature and multifunctional performance, 3D graphene foam has become a promising material for nextgeneration energy storage, thermal management, sensors, catalysis, and multifunctional composite systems.
1. Concept of 3D Graphene Foam
3D graphene foam is produced by assembling graphene layers into a continuous threedimensional macrostructure. Unlike conventional twodimensional graphene powder or nanosheets, the foam maintains a stable, opencell network that preserves graphene’s intrinsic properties while overcoming aggregation issues common in 2D materials. The resulting material exhibits both nanoscale graphene characteristics and macroscale structural advantages, enabling high conductivity, flexible mechanical behavior, and rapid mass transport.
2. Structural Characteristics
• Interconnected Porous Network
The structure consists of graphene walls forming an opencell foam with pore sizes typically ranging from micrometers to hundreds of micrometers. This architecture ensures high permeability, low density, and large accessible surface area.
• GrapheneBased Cell Walls
The foam’s skeleton is made of singlelayer or fewlayer graphene sheets, providing exceptionally high strengthtoweight ratio, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity.
• Tunable Density and Morphology
Density can vary from 5 mg/cm³ to 100 mg/cm³ depending on synthesis methods, allowing customization for specific mechanical, electrical, and chemical requirements.
• Hierarchical Structure
Many 3D graphene foams exhibit micro, meso, and macroporosity simultaneously, beneficial for catalysis, adsorption, and electrochemical applications.
3. Key Material Properties
• UltraLow Density
3D graphene foam is among the lightest solid materials, with densities comparable to aerogels and carbon foams.
• Exceptional Conductivity
The interconnected graphene network enables high electrical conductivity (up to several thousand S/m) and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for electrodes and heat spreaders.
• High Mechanical Resilience
The foam can withstand large compressive strains and recover its shape due to the elasticity of graphene sheets and the robustness of the 3D skeleton.
• High Surface Area
Specific surface areas typically range from 500 to 2000 m²/g, significantly improving reaction activity and charge storage capacities.
• Chemical and Thermal Stability
Graphene’s inert structure resists corrosion, oxidation (in controlled environments), and thermal degradation.
4. Manufacturing Processes
Several fabrication methods are commonly used:
• Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Graphene is grown on 3D metal templates (such as nickel foam), which are later etched away. This method produces highquality, ultrathin graphene networks with excellent conductivity.
• FreezeCasting and Hydrothermal Assembly
Graphene oxide suspensions selfassemble into porous structures during freezedrying or hydrothermal reduction, forming lightweight, costeffective foams.
• 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
Advanced methods allow controlled design of pore size and foam geometry, enabling custom structures for specialized engineering applications.
• TemplateAssisted Synthesis
Polymeric or ceramic templates create predefined pore structures by carbonization and reduction.
Each technique influences foam density, conductivity, purity, and mechanical strength.
CVD Graphene Foam
5. Applications of 3D Graphene Foam
• Energy Storage
3D graphene foam serves as an electrode framework in lithiumion batteries, sodiumion batteries, supercapacitors, and solidstate batteries. Its high surface area enhances charge storage, while the conductive network improves ion/electron transport.
• Thermal Management
Used as heat spreaders, thermal interface materials, and lightweight heat dissipation substrates in electronics and aerospace systems.
• Catalysis and Electrocatalysis
The large surface area and open channels support catalyst particles, improving reaction efficiency for fuel cells, CO₂ reduction, water splitting, and organic synthesis.
• Sensors
3D graphene foam’s sensitivity to strain, pressure, gas molecules, and temperature enables highly responsive mechanical, chemical, and electrical sensors.
• Environmental Applications
Serves in adsorption of heavy metals, organic pollutants, and oil spills due to its large surface area and hydrophobic properties.
• Biomedical Engineering
Used for drug delivery, tissue scaffolding, and biosensing, thanks to its biocompatibility and porous architecture.
• Composite Reinforcement
Incorporated into polymers, metals, or ceramics to enhance conductivity, mechanical properties, and thermal stability.
6. Advantages
• Superior Multifunctionality
Combines electrical, thermal, mechanical, and chemical performance in one material.
• Lightweight and High Strength
Offers excellent robustness while maintaining extremely low density.
• High Efficiency in Electrochemical Systems
3D pathways reduce internal resistance, improving energy/power density.
• Tunable Structure
Pore size, thickness, density, and surface chemistry can be customized.
• Strong Stability
Maintains performance under mechanical compression, thermal cycling, and chemical exposure.
• Scalable Fabrication
Advancements in hydrothermal and freezecasting techniques enable costeffective largescale production.
Conclusion
3D graphene foam represents a groundbreaking material that bridges the gap between nanoscale graphene properties and macroscale engineering requirements. Its unique 3D interconnected network delivers exceptional conductivity, high strength, lightweight structure, and broad application potential across electronics, energy storage, catalysis, environmental engineering, and advanced manufacturing. With its tunable architecture and outstanding multifunctional performance, 3D graphene foam continues to play an increasingly important role in nextgeneration materials science and industrial innovation.